Smussamento bordi
Migliore adesione del rivestimento e minor rischio di lesioni
SBM-XS G1E1
Lavorazione su entrambi i lati di pezzi piccoli - Sbavatura e arrotondamento uniforme di tutti i bordi die pezzi sui contorni esterni ed interni in un'unica fase di lavoro
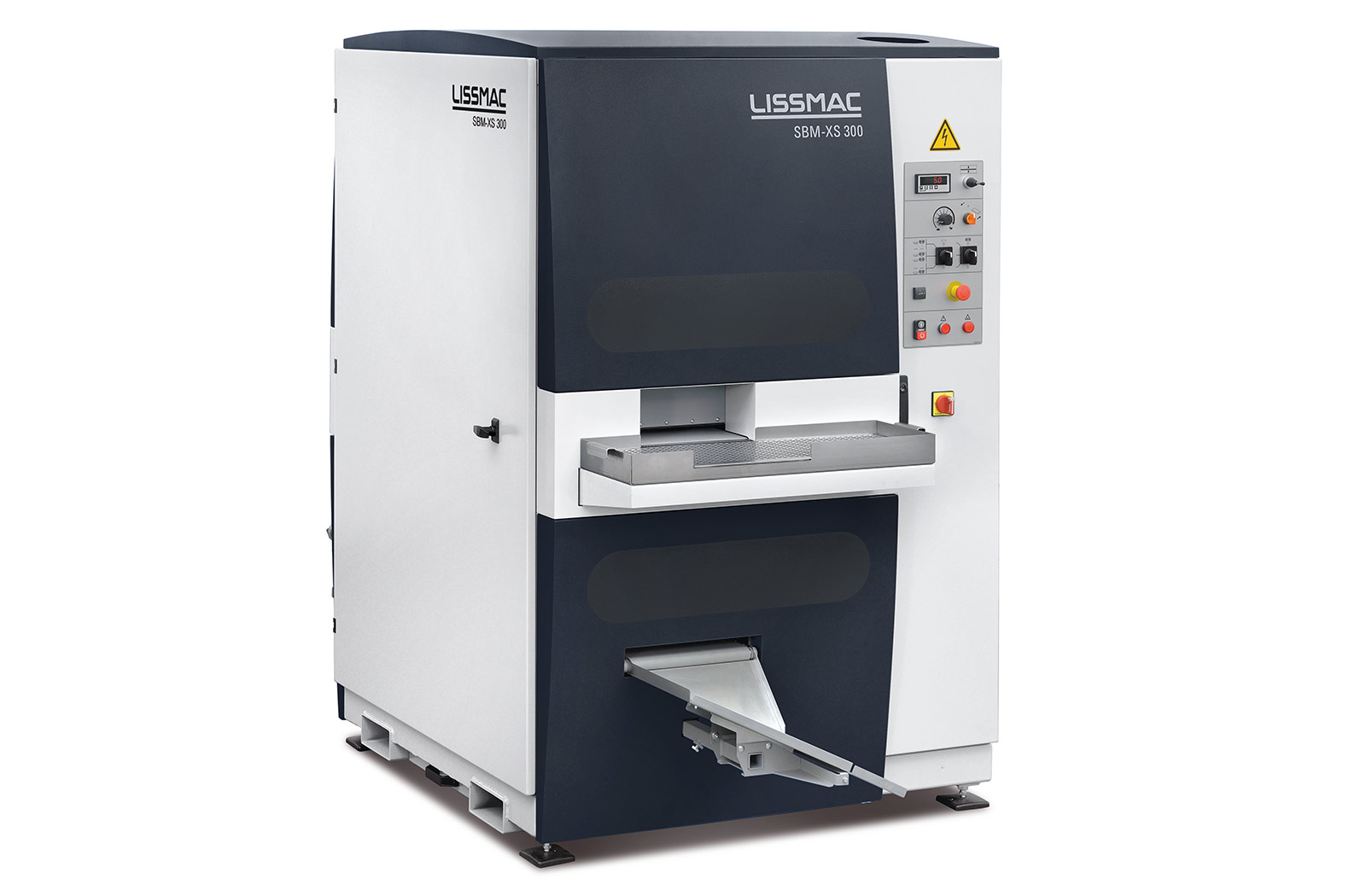

SBM-M S2
Sbavatura e arrotondamento su entrambi i lati, in un unico processo, dei bordi di lamiere di acciaio e acciaio inox
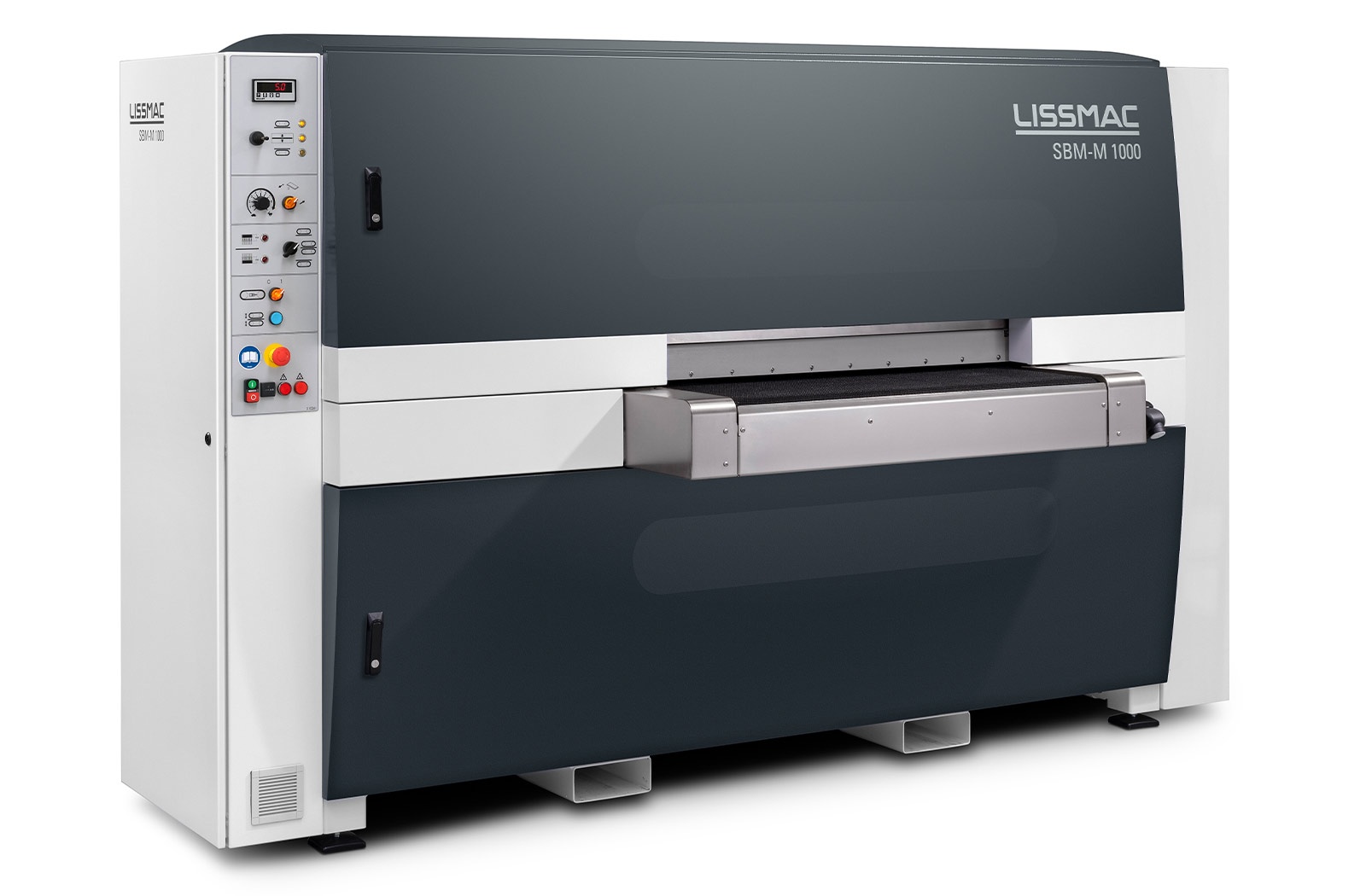

SBM-M D2
Rimozione di scorie su entrambi i lati, in un unico processo, da pezzi tagliati con utensili al plasma o autogeni
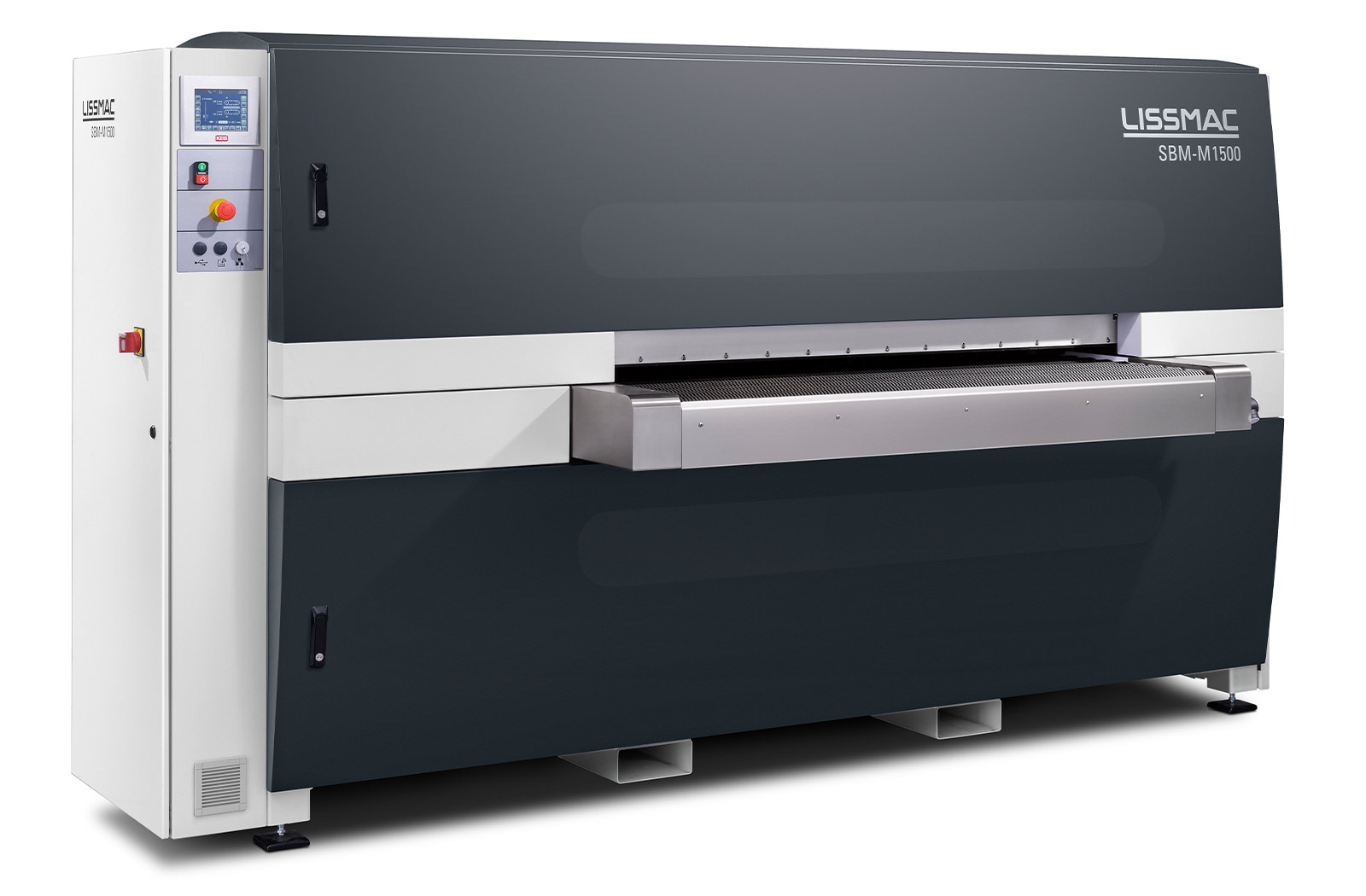

SBM-L G1S2
Sbavatura e arrotondamento dei bordi su entrambi i lati di elementi stampati, tagliati al laser e al plasma in un unico processo operativo
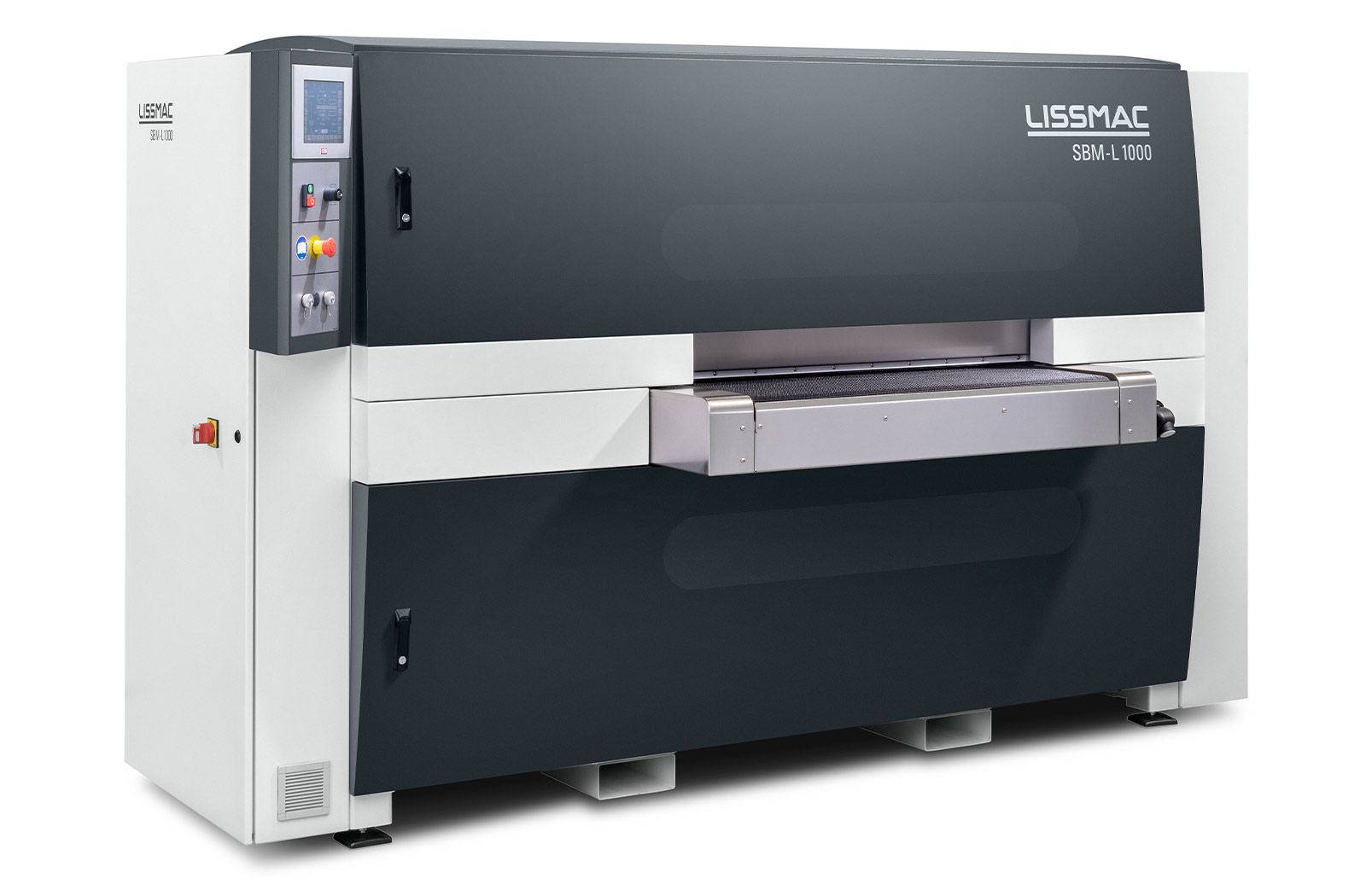

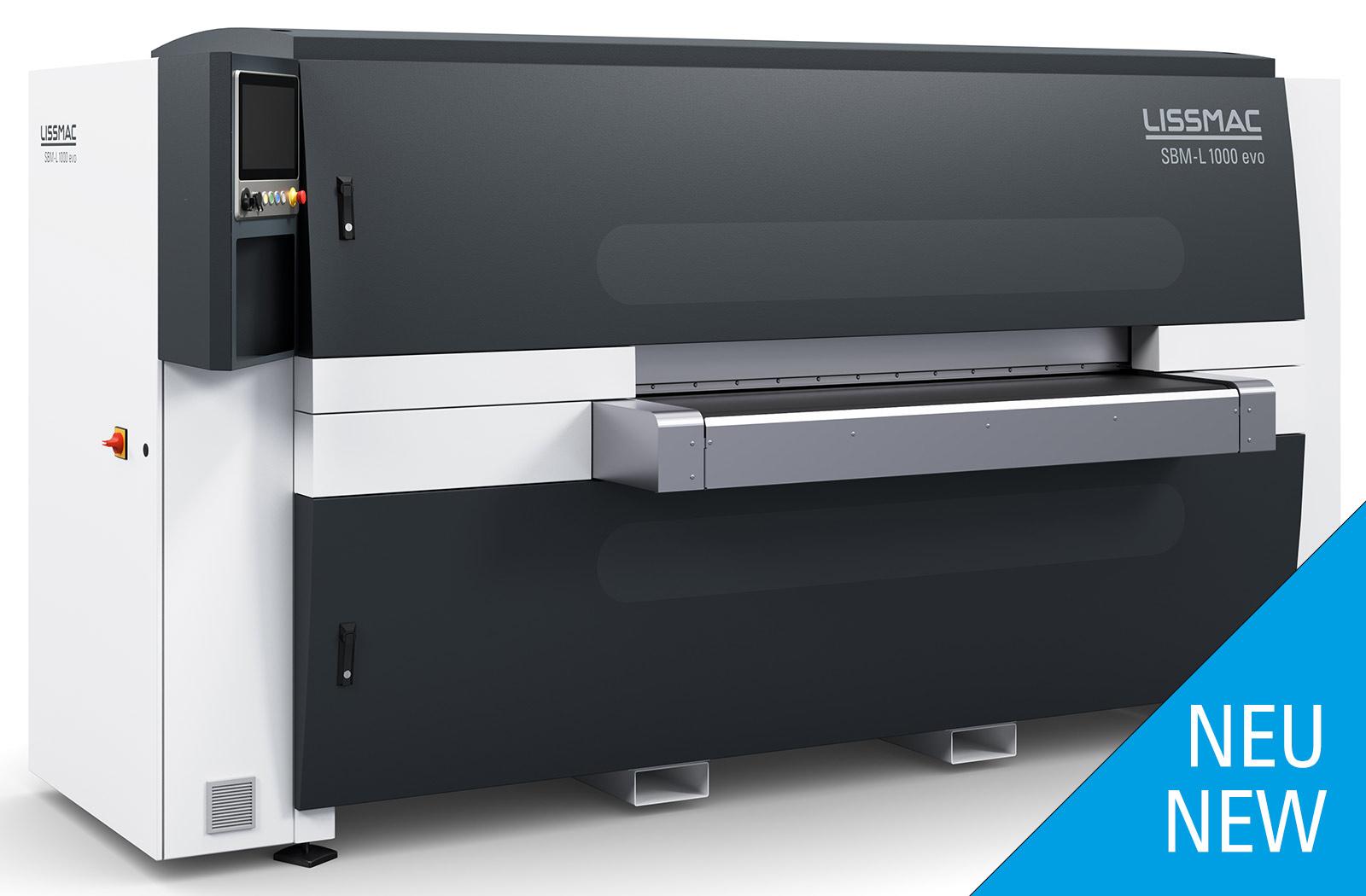
SBM-L G1S2 EVO
Sbavatura e arrotondamento dei bordi su entrambi i lati di elementi stampati, tagliati al laser e al plasma in un unico processo operativo

SBM-XL G2S2
Arrotondamento dei bordi e sbavatura su entrambi i lati, in un unico processo, di pezzi tagliati con utensili autogeni, al plasma e laser
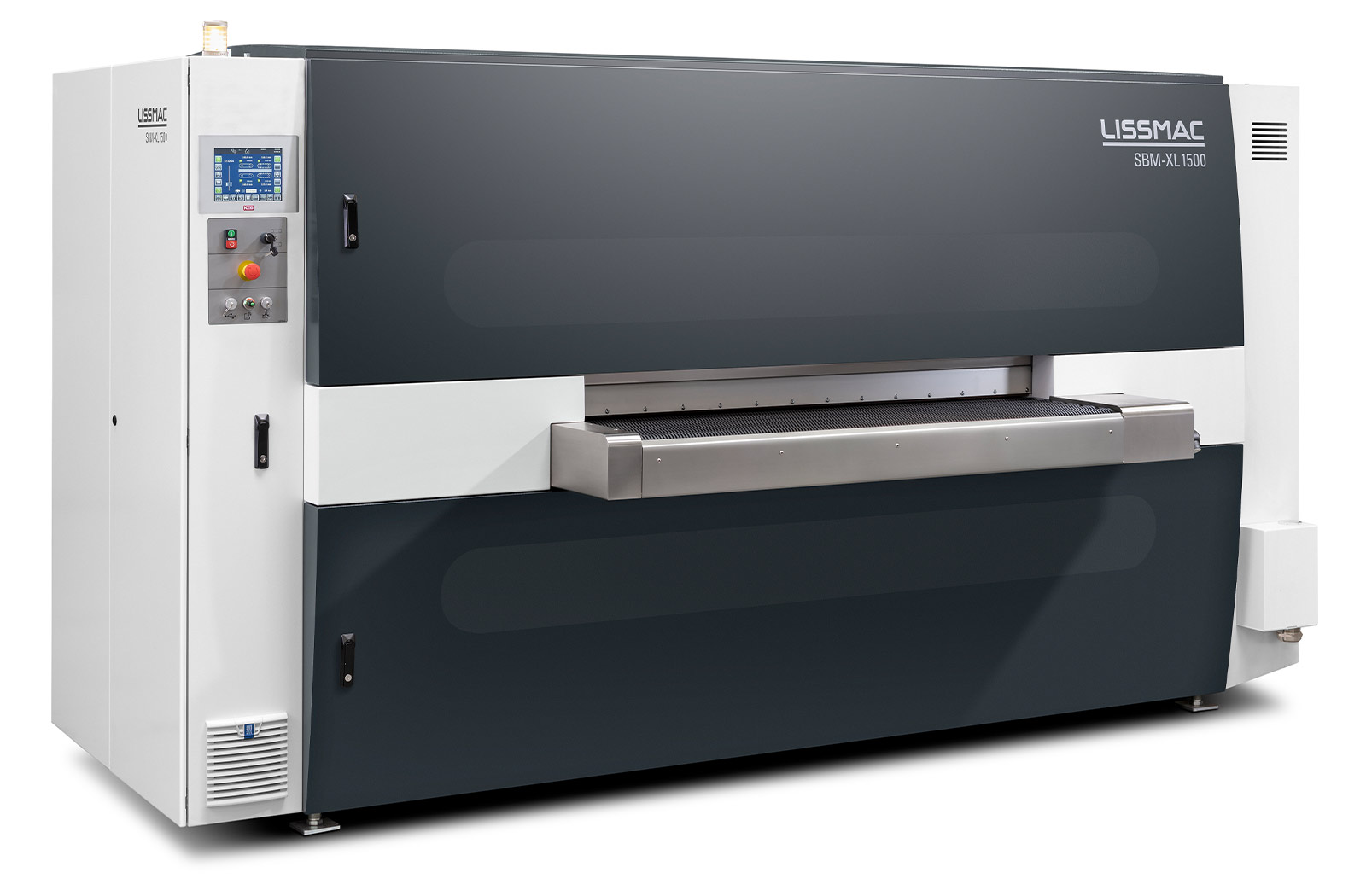

SMD 123 RE
Dry grinding machine for deburring, consistent edge rounding and surface finishing
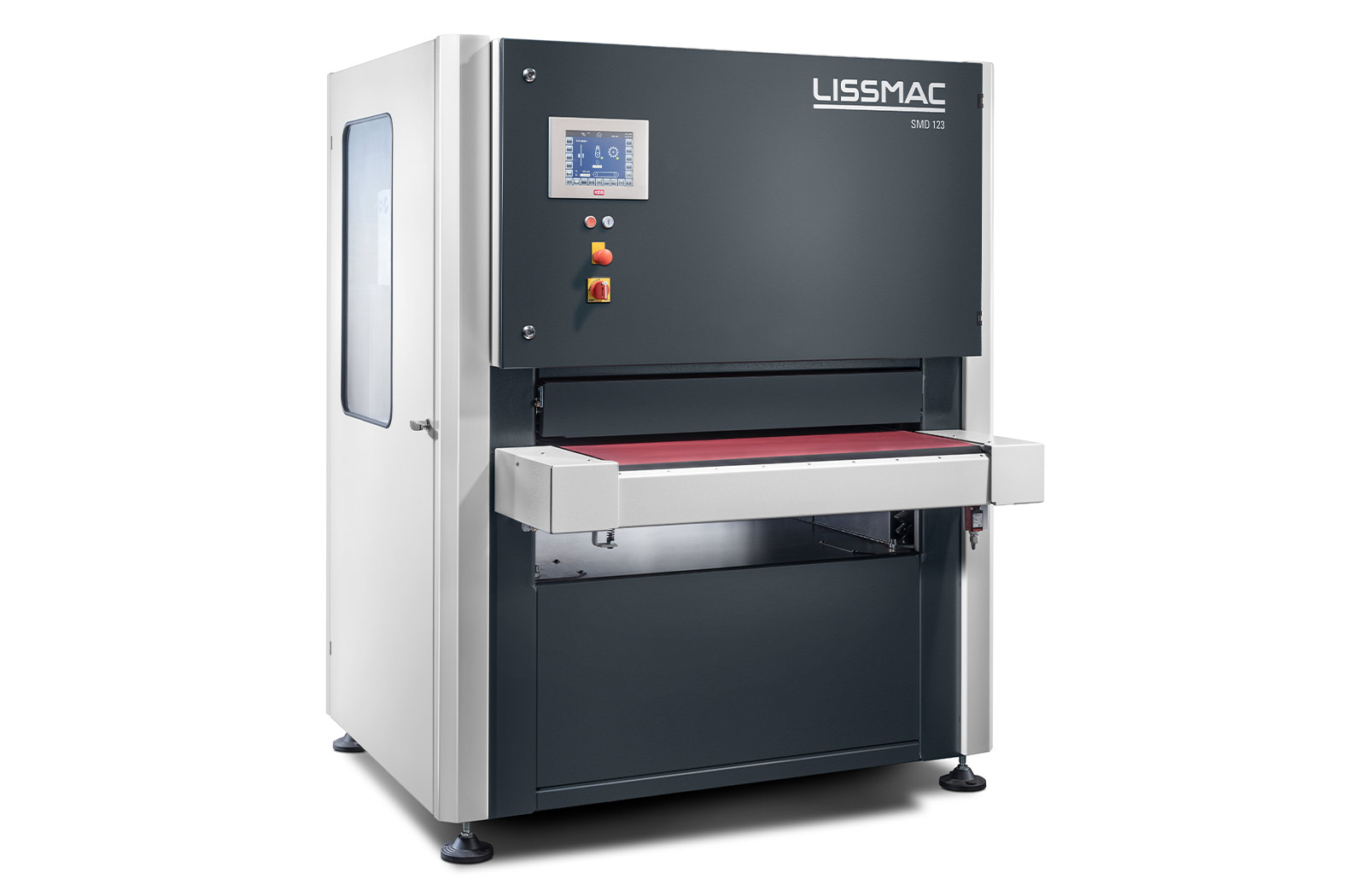

SMD 133 DRE
Eliminación económica de la escoria, el desbarbado y el redondeo de los bordes en las piezas cortadas por plasma y oxicorte
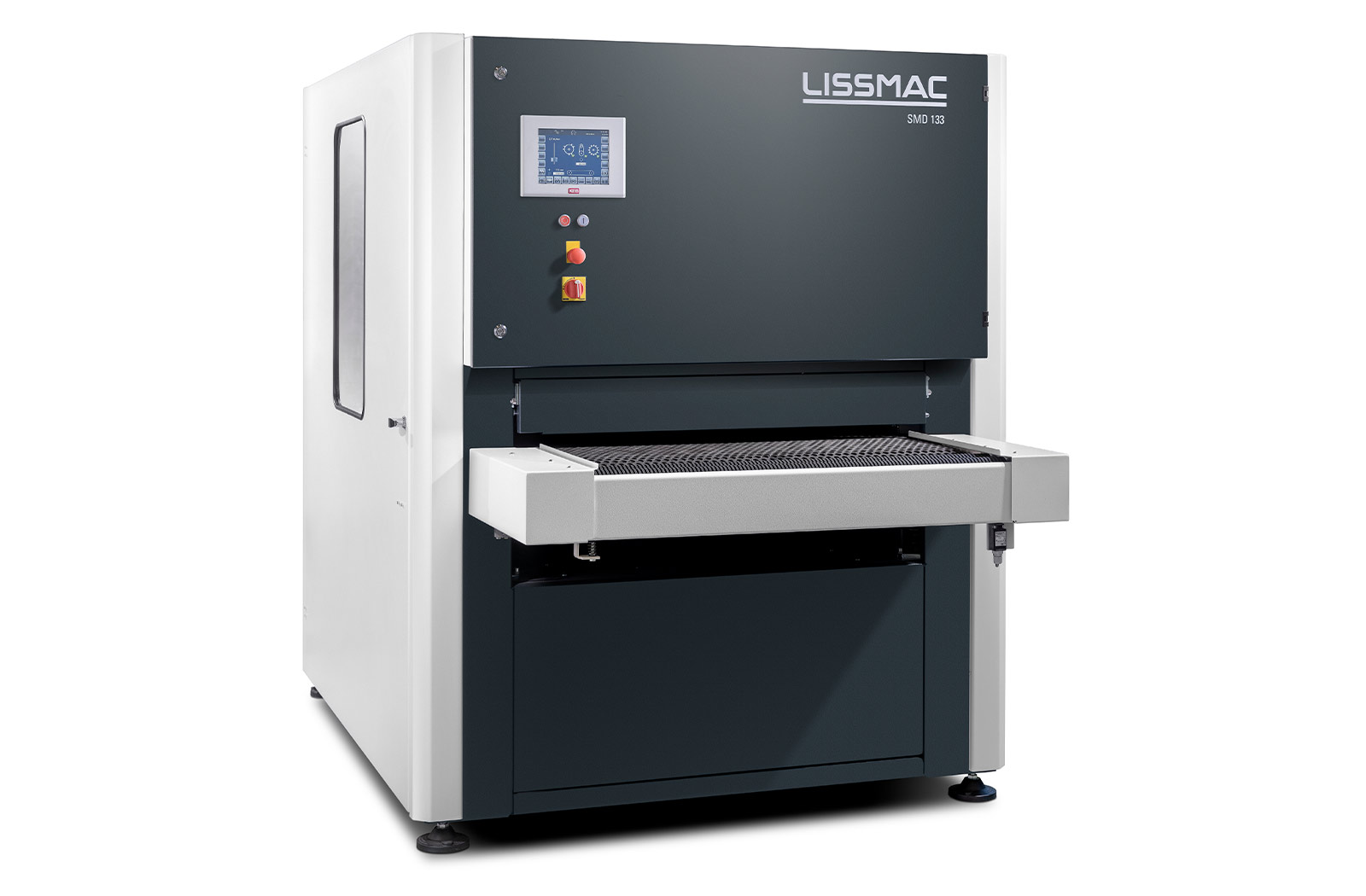

SMD 3 S - EDITION
Risultati eccezionali sul bordo e sulla superficie
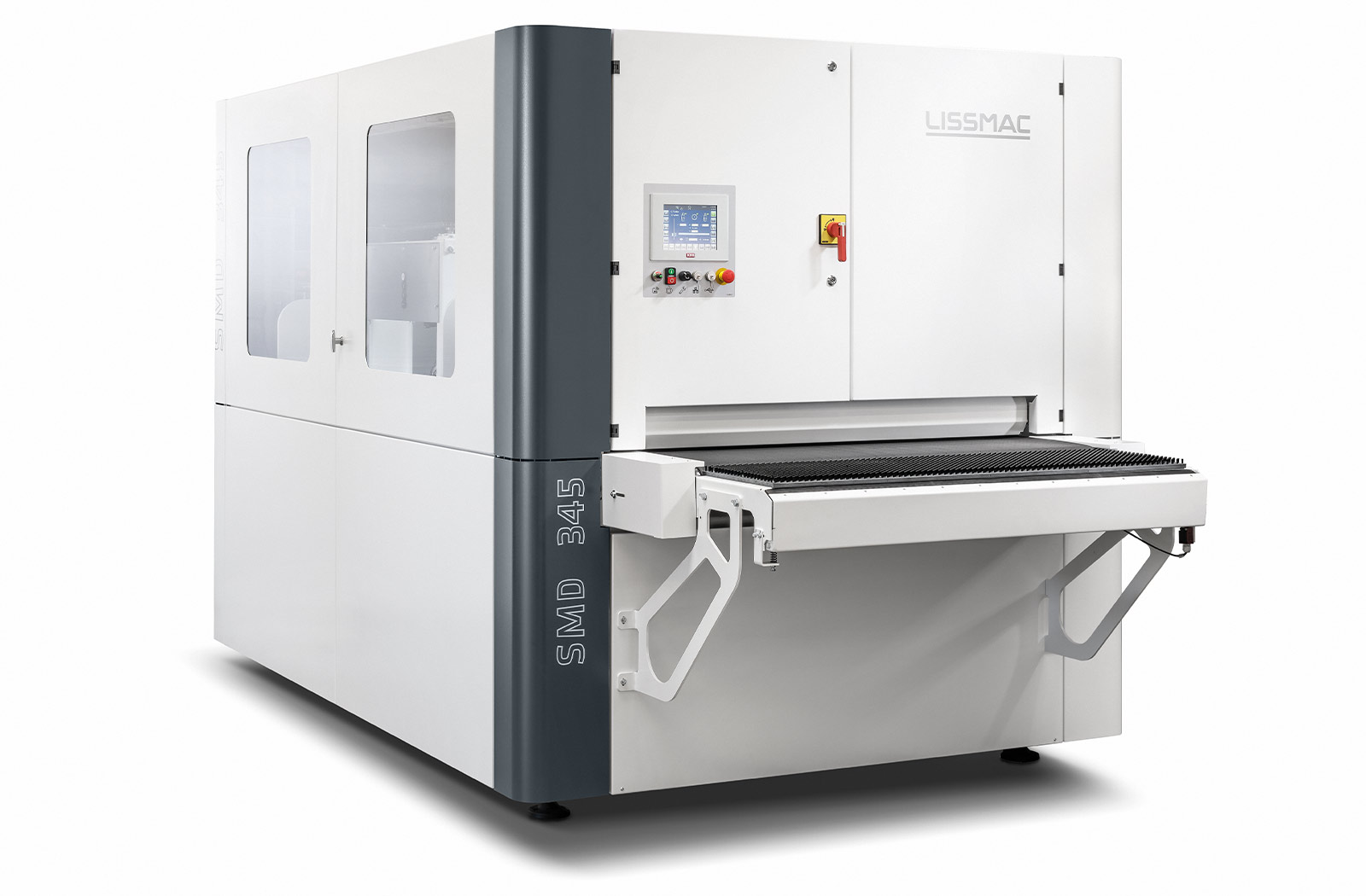

SMD 3 P - EDITION
Consistente arrotondamento del bordo
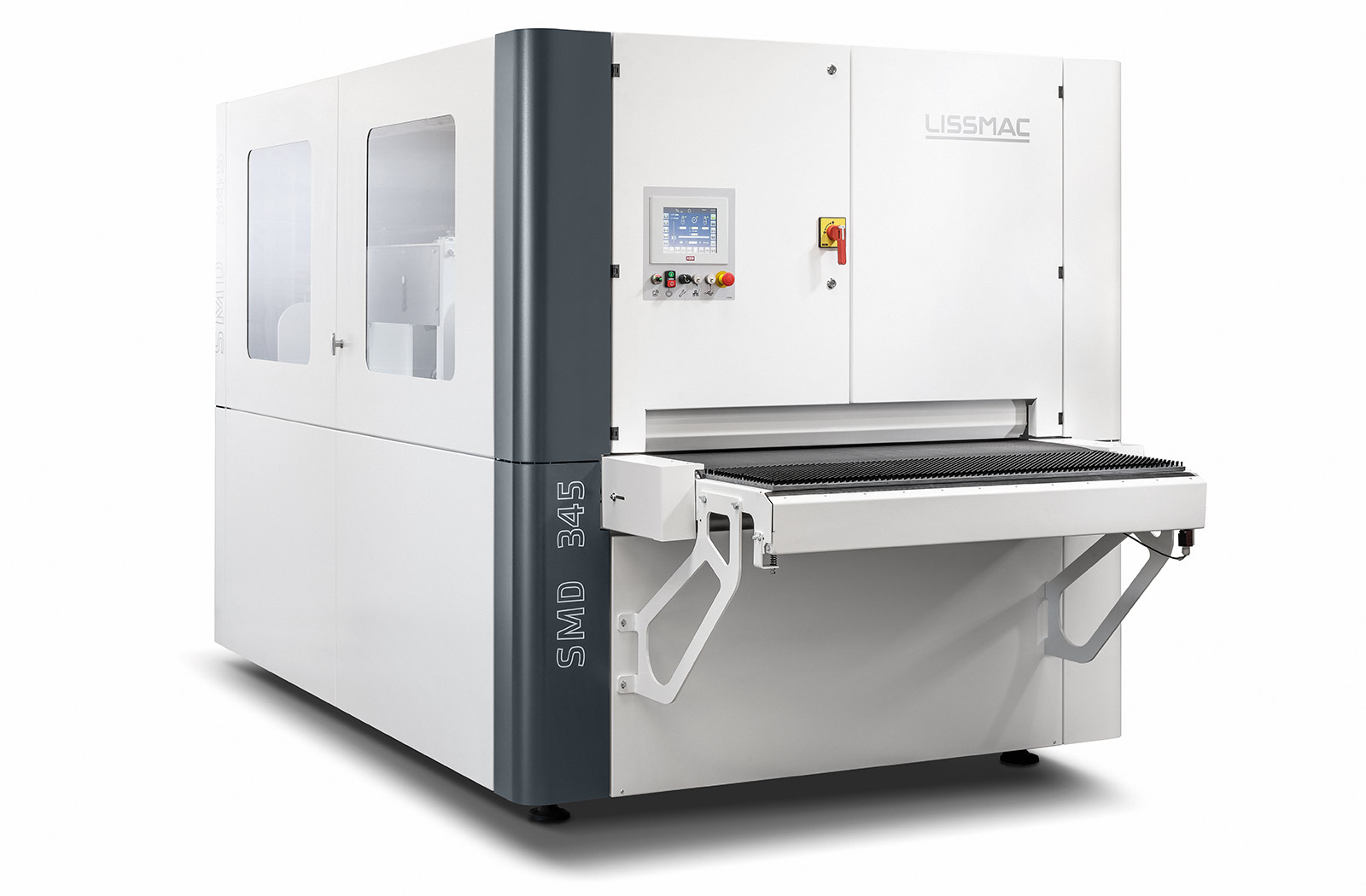

SMW 5
Maccina smergliatrice sul bagnato che rettifica il processo per la macinazione della superficie superiore dei pezzi

Why Edge Rounding Matters in Modern Industries
In modern metalworking industries, precision, safety, and surface quality are paramount.
Cutting, punching, or laser processing of sheet metal inevitably creates sharp edges and burrs. These not only pose a significant risk of injury but also impair the adhesion of paints and powder coatings.
This is where edge rounding becomes essential.
Edge rounding, also known as edge breaking, is the controlled process of removing burrs and creating consistent, defined rounded edges on all inner and outer contours of a workpiece. This improves coating adhesion and contributes to a higher overall product quality. By ensuring uniform edge geometry, edge rounding is essential for meeting increasing customer expectations regarding surface finish and durability, while also preparing components for optimal downstream processing.
The Edge Rounding Process
1. Workpiece Transport – Foundation for Precision
To achieve consistent and high-quality edge rounding, the metal parts must first be securely guided through the machines. Depending on the size, material, and shape of the metal parts, edge rounding machines are equipped with different transport systems:
PowerGrip Conveyor Belt – ideal for small or embossed metal parts, highly energy-efficient and versatile
Vacuum Table – perfect for large, sensitive metal sheets that require gentle handling
Magnetic Track – provides strong holding force for ferromagnetic steel components
These transport systems ensure stable positioning of metal parts and support accurate processing across a wide range of machines used in the edge rounding workflow.
2. Preprocessing
Before edge rounding takes place, burrs are removed using long or wide belt grinding belts. Slag and oxide layers are thoroughly removed by PowerPins and brush belts.
This step also helps eliminate secondary burrs that can compromise surface quality and downstream performance.
3. Edge Rounding - edge radius of 2 mm
In the next step, the actual edge rounding is carried out – up to a radius of 2 mm. Depending on the requirements, either sanding belts or round flap brushes are used: sanding belts provide powerful, even rounding on larger surfaces, while round flap brushes allow for precise, contour-adapted processing of even complex geometries. This precise edge rounding creates safe, smooth surfaces that excel in both surface quality and durability. The result: increased handling safety, a pleasant tactile feel, and perfect surfaces for subsequent coatings.
Additionally, the edge rounding reliably meets specific customer requirements for defined rounding radii.
Sharp Edges: Typical Applications
Edge finishing is widely used, especially where precision and finish quality are essential. Common applications include:
- Laser-cut sheets made of stainless steel, steel, or aluminum
- Punched and plasma-cut parts
- Boreholes, inner and outer contours
- Foiled parts
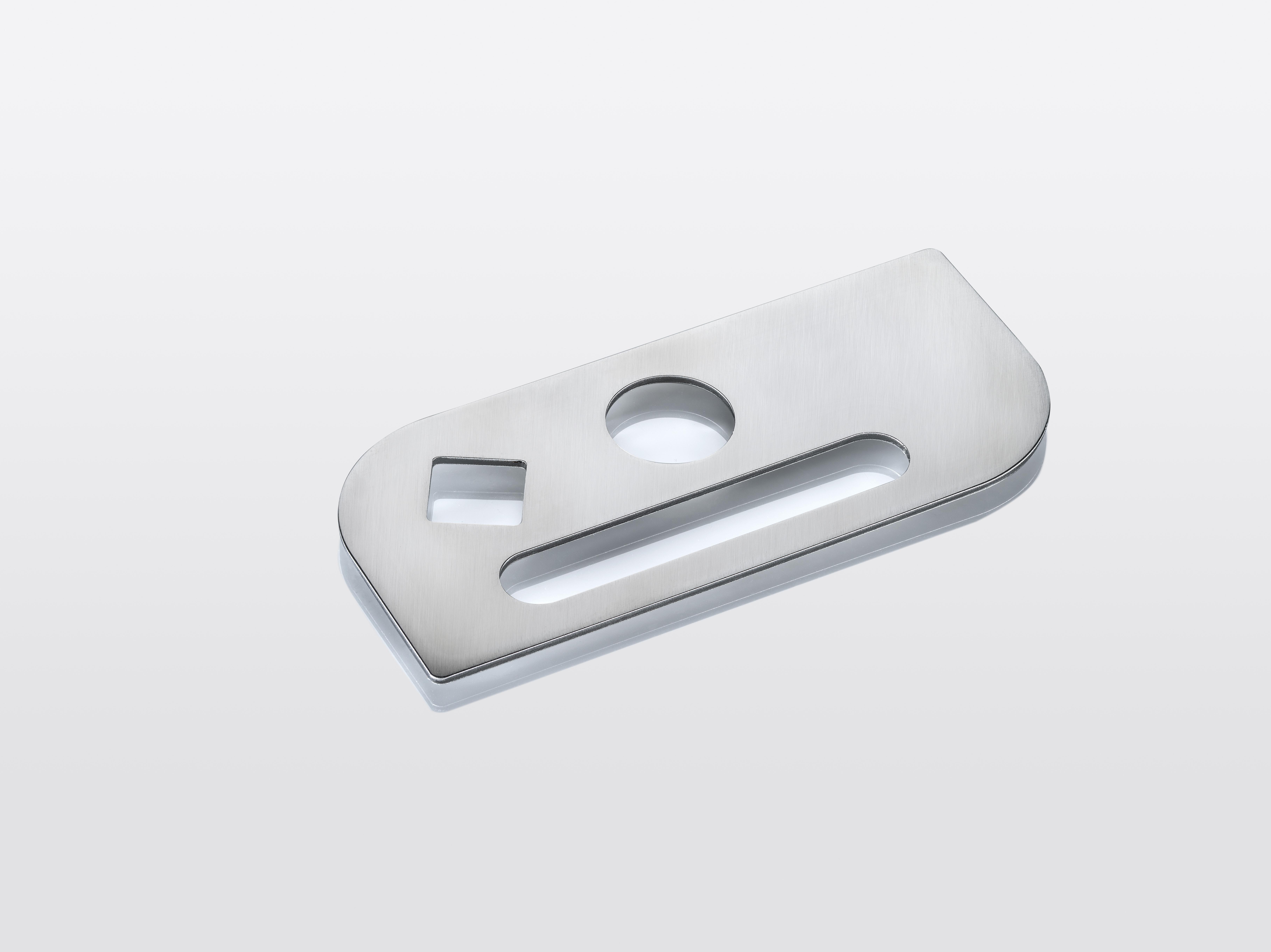
Sheet metal with edge rounding on both sides, processed on a LISSMAC SBM-M S2. The machine removes burrs and ensures uniform rounding of both internal and external contours.

How Optimal Edge Rounding Creates Perfectly Rounded Edges – Why LISSMAC Makes the Difference
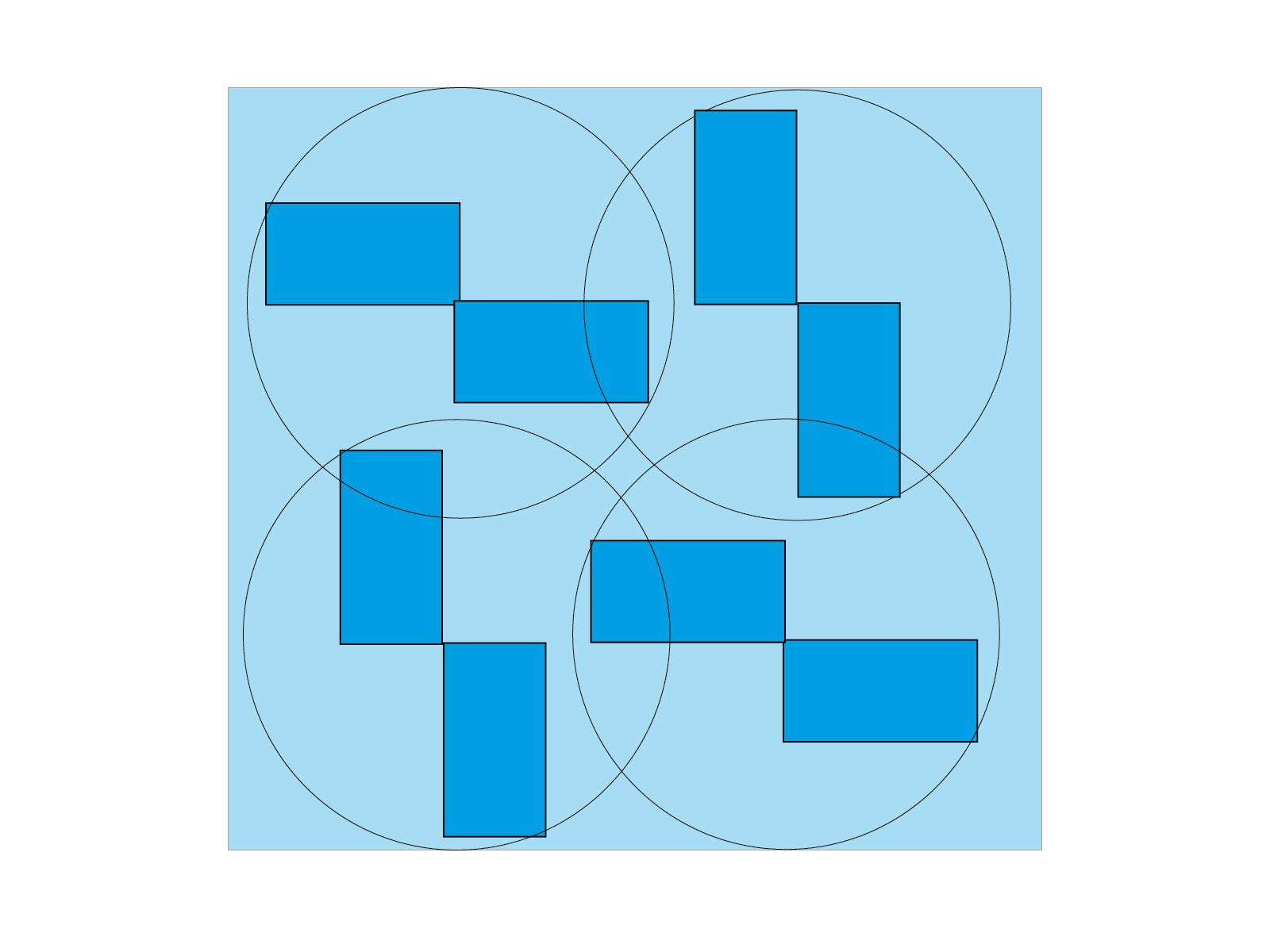
The SMD 3 series from LISSMAC impresses with its innovative, overlapping rotation system. This machine concept, featuring four rotating brush heads, enables uniform edge rounding of metal and sheet metal parts on all inner and outer contours—regardless of the part’s geometry, material, or shape. The result is a consistent edge radius across the entire working width, from 300 to 2000 mm. In combination with efficient grinding and deburring steps, users benefit from high process reliability, flexibility for a wide variety of components, and significantly improved energy efficiency.
With this, LISSMAC sets new standards in modern edge processing, ensuring consistently excellent results in both functionality and surface quality.
On the left side of the image, you can see the LISSMAC rotation system – equipped with four overlapping, rotating brush heads that ensure consistent, high-quality results. The system shown on the right, on the other hand, works with several brushes that rotate around a central axis. This can result in less rounding at the edges of the conveyor belt, while stronger rounding occurs under the central axis.